Reserch Projects
Magnetic gears and high torque actuators
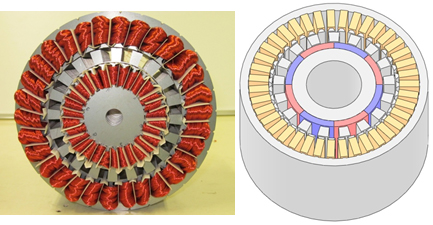
・Magnetic-geared motors
 |
Magnetic geared-motors are low speed high torque motors of the next geeration that have a higher output that conventional motors. By optimising the configuration of the permanent magnets, high torque densities can be obtained with a minimum amount of permanent magnets. |
poster
・Magnetic-geared generators
| Renewable energy has been attracting more and more attention. Wind power generation is one of the most promising forms of renewable energy. We are now developing a novel generator to solve the disadvantages of the traditional systems. Our proposed generator is both compact and maintenance free because step-up gears are not required in our proposed system due to the high EMF constant of our generator. |
poster
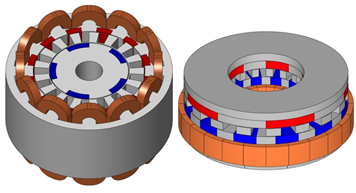
・Magnetic-geared CVT motor
 |
The gear ratio of previous magnetic-geared motors is constant, but that of the magnetic-geared CVT motor is variable. The high-speed rotor is driven by 3-phase AC currents and the output rotation speed of the low-speed rotor can be changed by controlling the frequency of 6-phase AC currents. The previous magnetic-geared motors have low speed and high torque characteristics. However, the magnetic-geared CVT motor has wide power band characteristics. |
poster
・Two-controllable-rotor motors
| This motor has two rotors and one stator. The two rotors can be independently controlled using two kind of 5-phase superimposed currents created by a 5-phase inverter. In a machine with multiple outputs, the space of the motors and their inverter are reduced. |
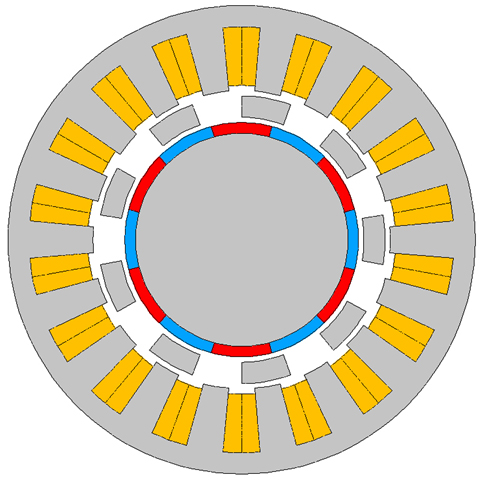
・Magnetic gears
 |
We have been researching magnetic gears that utilize magnetic flux harmonics. From the original surface permanent magnet type, we have been researching the hybrid type that borrows its structure from the stepping motor, to the axial magnetic gear, and also the magnetic CVT which has a continuously variable gear ratio. |
poster
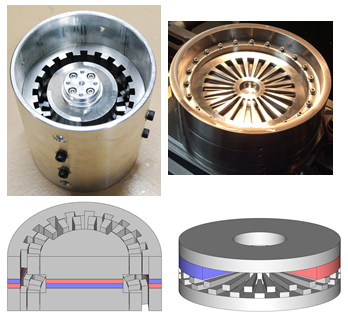
・Magnetic gears with variable gear ratio
 |
We have been researching magnetic gears which have variable gear ratios. We have been researching the magnetic gear which has some gear ratio and a continuously variable gear ratio. |
poster
・Differential magnetic gears
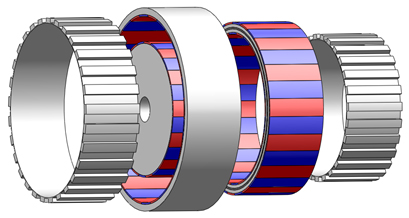 |
The gear ratio of magnetic gears depends on the number of pole pairs of both rotors. Therefore, it was difficult to design a high-gear-ratio magnetic gear in terms of the structure. We could develop a magnetic gear by using a differential mechanism, which has a high gear ratio (from several dozens to several hundreds). This differential magnetic gear can be classified to axial and radial types. |
・Differential Magnetic-Geared Motors
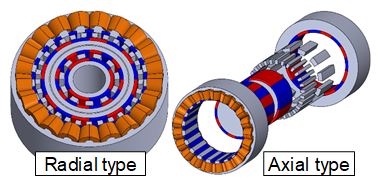 |
Magnetic geared motors attract attention due to its low-speed and high-torque characteristics. However, the increase of the number of pole pairs decreases the torque density. In order to solve this problem, differential magnetic-geared motor that is combined a magnetic geared motor with a magnetic gear has been proposed. This differential magnetic-geared motor can be classified to axial and radial types. |
・Magnetic planetary gears
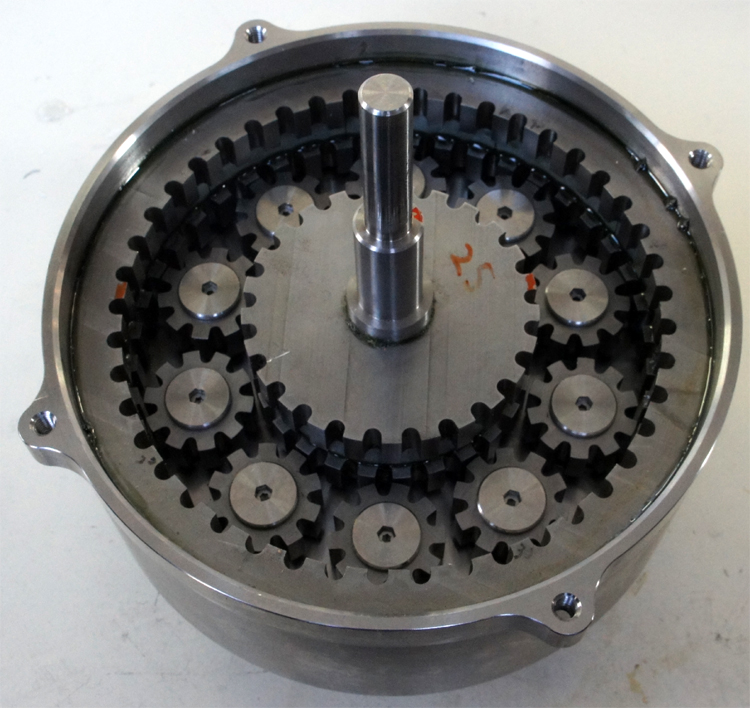 |
Planetary gears are widely used due to their high gear ratios. We are conducting research on the magnetic version of this, and also the magnetic version of the paradox gear, which is an expansion of the planetary gear and can obtain a very, very high gear ratio. |
poster
・Magnetic impact devices
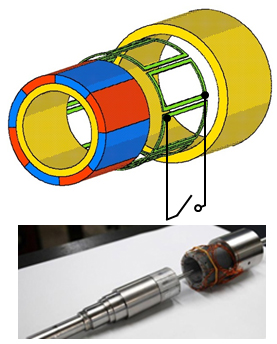 |
In conventional impact mechanisms, the impact torque is generated from the hammer connected to a motor beating the anvil block. Therefore, a large amount of noise is generated due to the collision between the two metal bodies. We are conducting research on a non-contact electromagnetic impact-torque mechanism using induced current. |
poster
・Magnetic pulleys
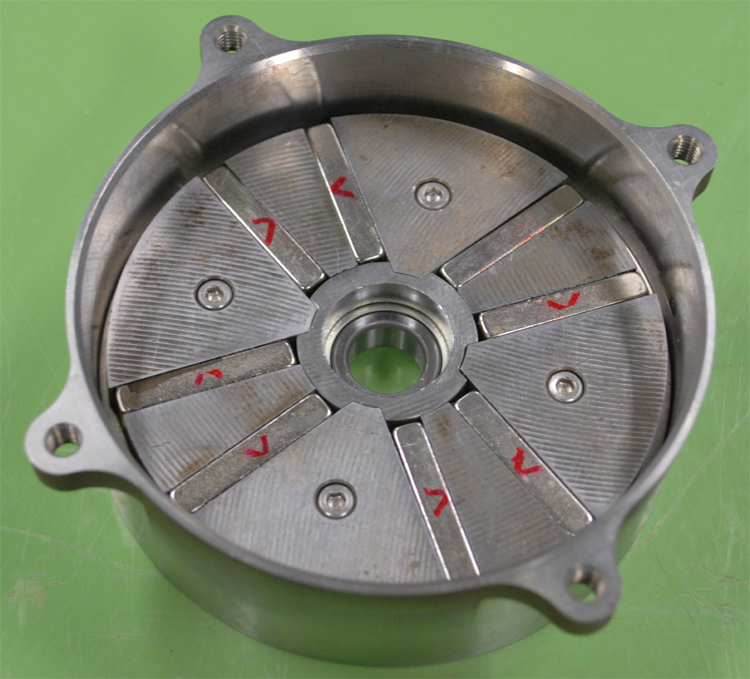 |
Conventionally, the torque from an engine is transferred to the load through a belt. The vibration from the engine is absorbed by a mechanical spring. However the transmission torque is determined by the spring characteristics. We are studying magnetic pulleys whose torque curve can be arbitrarily designed. |
